Docker Repository Cleaning
Your Docker Repositories can become full of old images that you don’t need anymore. Left unchecked these images can take up considerable space and cost a considerable amount of money. When deploying images with continuous integration this cost can explode.
Cost Calculator
Deleting Risk
Deleting images comes with some risk. If there are containers using an image, and it is deleted from the repository, you may not be able to recreate the container. When using Kubernetes or AWS ECS containers can be rebuilt during cluster maintenance or auto scaling.
No Docker Command to Delete
In Docker there is no native way to delete a tag from a repository. This is good for public image or source code repositories. If lots of things are depending on another and it gets deleted, all of the users will have broken dependency. This is what happened with the npm left-pad debacle.
But for your private docker repositories where you control all of the usages of an image, you want to be able to delete old images.
How to Safely Delete Docker Images
- Don’t delete images that are in use or that you might need soon. Often it is ok to assume that only the most recent will be needed.
- Keep the last 5 snapshot builds
- Keep the last 10 non-snapshot builds
- Keep the “latest” tag
- Delete anything else
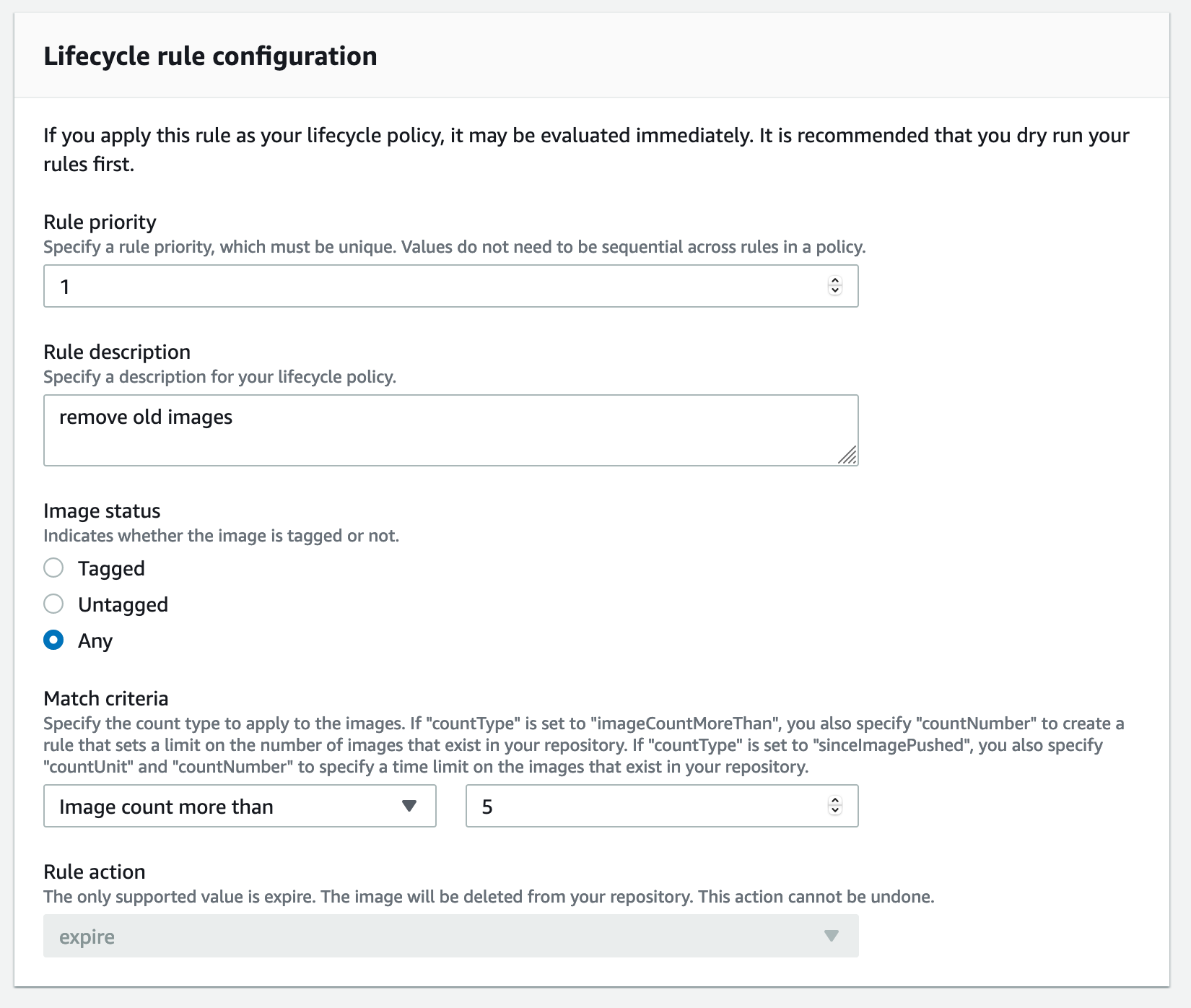
AWS Lifecycle Rules
AWS provides lifecycle rules which can delete old images, but it does not have the smarts to check if an image is still in use by a running container or if it is a SNAPSHOT or latest build. So you are left with the assumption that only the last N builds are important and crossing your fingers.
AWS ECR Cleaning Script
You can build a bash simple script using the aws cli command to delete old images. You can filter for SNAPSHOT and latest. However this is still using the assumption that only the most recent are important.
#!/usr/bin/env bash
REPOSITORY="repo"
MAX_SNAPSHOTS=5
MAX_NON_SNAPSHOTS=10
images=$(aws ecr describe-images --repository-name "$REPOSITORY")
sortedImageTags=$(echo "$images" | jq -r '.imageDetails | sort_by(.imagePushedAt) | reverse | .[].imageTags[]')
snapshotsToDelete=$(echo "$sortedImageTags" | grep SNAPSHOT | tail -n +$MAX_SNAPSHOTS)
nonSnapshotsToDelete=$(echo "$sortedImageTags" | grep -v "SNAPSHOT" | grep -v "latest" | tail -n +$MAX_NON_SNAPSHOTS)
allToDelete=$(echo "$snapshotsToDelete $nonSnapshotsToDelete" | sed 's/.*/imageTag=&/' | tr '\n' ' ')
aws ecr bulk-delete-images --repository-name $REPOSITORY "$allToDelete"
Happy Hacking
If you liked this article and want more tips, follow me on twitter @hi_stephen_n 💙